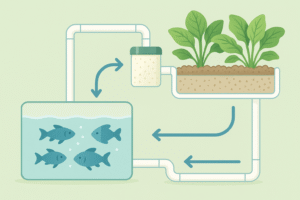
Key Components of an Aquaponics System
-
- Fish Tank — Houses fish; their waste initiates the nutrient cycle.
-
- Grow Beds — Hold plants and a growing medium (e.g., clay pebbles) for root support.
-
- Nitrifying Bacteria — Convert toxic ammonia → nitrites → nitrates, which plants absorb.
-
- Water Circulation System — Pumps water between tank and beds, forming a closed-loop cycle.
-
- Optional Aeration & Monitoring — Air stones, sensors, or IoT devices to boost oxygen and track pH.
How Does Aquaponics Work?
-
-
- Fish Waste Production: Fish excrete ammonia-rich waste into the water.
-
- Bacterial Conversion: Beneficial bacteria transform ammonia into plant-friendly nitrates.
-
- Plant Filtration: Plants absorb the nitrates, cleaning the water.
-
- Water Recirculation: Purified water returns to the fish tank, completing the cycle.
Top Benefits of Aquaponics
-
- Resource Efficiency: Uses up to 90 % less water than traditional soil farming.
-
- Chemical-Free Produce: Eliminates synthetic fertilizers by leveraging natural nutrient cycles.
-
- Versatility & Scalability: Works in poor-soil regions—from balcony setups to commercial greenhouses.
-
- Sustainability: Minimizes environmental impact with near-zero waste output.
Common Fish & Plant Species
Fish: Tilapia (hardy, fast-growing), catfish, trout, or ornamental species like goldfish.
Plants: Leafy greens (lettuce, kale), herbs (basil, mint), and fruiting crops (tomatoes, cucumbers).
Key Challenges & Best Practices
-
- Maintaining Balance: Monitor pH, ammonia, nitrites, nitrates regularly.
-
- System Interdependency: Fish, plants, and bacteria must coexist harmoniously.
-
- Initial Investment & Know-How: Requires upfront equipment costs and ecological understanding.
Real-World Applications
-
- Scalable Farming: From urban home systems to large commercial operations.
-
- STEM & Entrepreneurship: Popular in schools for hands-on science and with startups producing premium fish & greens.
Aquaponics embodies a closed-loop ecosystem—leveraging natural processes for efficient, healthy food production.
Contact us to learn how you can implement a custom aquaponics solution today.